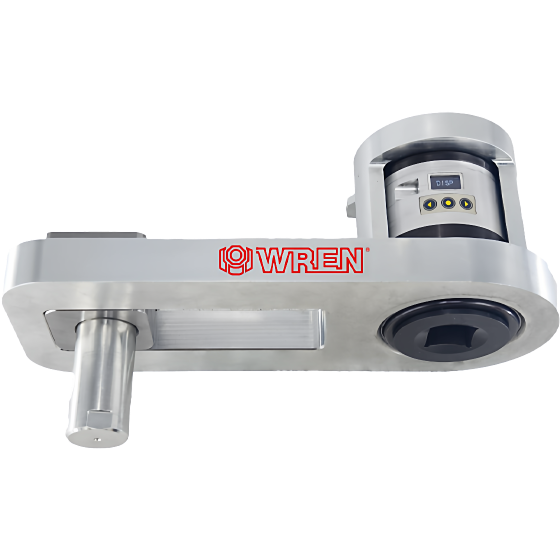
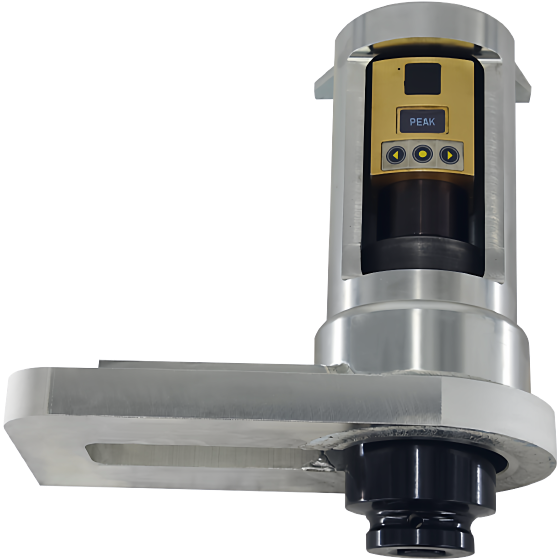
Through comparative analysis of electric pumps and electromagnetic pumps, electric pumps demonstrate significant advantages and are therefore widely adopted in the modern automotive industry.
High Oil Delivery Pressure: Electric pumps can regulate oil delivery pressure via pressure valves, providing pressure that meets the low-pressure fuel system requirements of engines.
Electromagnetic pumps, relying on electromagnetic induction for reciprocating motion and vacuum suction, exhibit low oil delivery pressure (average 1.6 bar), poor exhaust and fuel supply performance, and offer no significant improvement in starting efficiency.
High efficiency and low energy consumption: Electric pump motors operate at high speeds with stable, smooth performance, maintaining a steady operating current of only 2-3A. This ensures high efficiency, stability, and low energy consumption.
Electromagnetic pumps employ pulsed operating currents (1 pulse/second, max 12A), causing copper wires to burn out and overheat under high currents, posing safety hazards. They exhibit low efficiency, high energy consumption, and significant noise.
Minimal Electromagnetic Interference: Electric pumps operate on an eccentric rotor pump principle driven by a motor. They cause no interference to other components and are unaffected by other electronic devices, ensuring stable operation of electronically controlled engines. The product is certified by Cummins Inc.
The high current and pulsed operation of electromagnetic pumps cause significant external interference, particularly detrimental to electronically controlled and intelligent engines. Their use is strictly prohibited in military applications.
Impact of Pulsed Current and Pressure: Electric pumps operate at high motor speeds with stable working currents between 2-3A, delivering smooth, shock-free performance. Electromagnetic pumps' pulsed operation (1 pulse/second, max 12A) subjects batteries and other engine electronics to repetitive current fluctuations, potentially causing damage. Fluctuating outlet pressure induces impact fatigue on low-pressure fuel system components, shortening their lifespan.
Impact of pump failure on the fuel system: Electric pumps utilize an internal pressure valve for recirculation and incorporate a separate check valve bypass circuit. This ensures the engine's low-pressure fuel system remains functional even if the pump fails. Electromagnetic pumps, however, route fuel through the pump itself. If the pump fails or components are damaged, fuel flow can become blocked, causing the engine to malfunction.
Control Methods: Electric pumps support direct on/off control, ignition switch control, and ECM control, making them suitable for electronically controlled engines. Brushless pumps enable intelligent control. Electromagnetic pumps currently only offer switch-based control.